In the competitive landscape of digital advertising, understanding key performance indicators (KPIs) is paramount. One of the most critical metrics for gauging advertising effectiveness is Return on Ad Spend (ROAS). This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of ROAS, providing you with a clear understanding of its calculation, interpretation, and optimization strategies. Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or just starting your advertising journey, mastering ROAS is crucial for maximizing your returns and achieving a positive ROI (Return on Investment). This guide will equip you with the knowledge to effectively measure, analyze, and improve your advertising performance using ROAS.
ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) is a vital metric that measures the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising. Calculating ROAS allows you to assess the efficiency and profitability of your advertising campaigns. This guide will cover various aspects of ROAS, including how it differs from ROI, factors influencing ROAS, industry benchmarks, and strategies to improve your ROAS performance. By understanding and effectively utilizing ROAS, you can make informed decisions about your advertising budget allocation and optimize your campaigns for maximum profitability. This knowledge is essential for businesses of all sizes seeking to thrive in the digital marketplace and achieve sustainable growth.
Defining ROAS and Its Importance
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) is a key metric used in digital advertising to measure the effectiveness of a campaign. It essentially tells you how much revenue you generate for every dollar you spend on advertising.
Understanding ROAS is crucial for any business that invests in online advertising. It provides valuable insights into the profitability of your campaigns and helps you make informed decisions about budget allocation and optimization.
A high ROAS indicates that your ad campaigns are generating a significant return on investment, while a low ROAS suggests that your campaigns may need adjustments to improve their performance. By tracking and analyzing ROAS, you can identify which campaigns are most effective and allocate your budget accordingly.
ROAS is not simply about generating revenue; it’s about maximizing profitability. It enables you to optimize your campaigns to achieve the best possible return, ensuring that your advertising budget is being used efficiently.
Calculating ROAS: A Simple Formula
Calculating ROAS involves a straightforward formula that helps you understand the return you’re getting from your advertising investment. It’s a crucial metric for evaluating campaign effectiveness and making informed decisions about budget allocation.
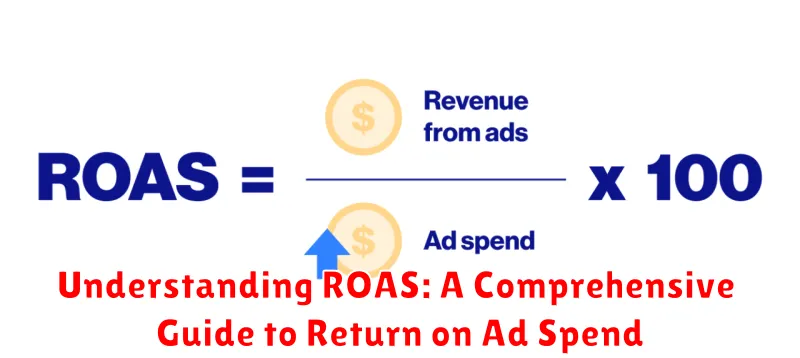
The basic formula for ROAS is:
ROAS = (Revenue Generated from Advertising / Cost of Advertising) * 100
For example, if you spent $1,000 on an advertising campaign and generated $5,000 in revenue, your ROAS would be:
ROAS = ($5,000 / $1,000) * 100 = 500%
This means that for every dollar you spent on advertising, you generated $5 in revenue.
Factors That Influence ROAS
Several key factors can significantly impact your ROAS. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing campaigns and achieving desired returns.
Industry Benchmarks and Competition
Industry benchmarks play a role in setting realistic expectations. Highly competitive industries often experience higher advertising costs, potentially lowering ROAS. Analyzing competitor strategies can provide insights into effective tactics and budgeting.
Targeting and Audience
Precise targeting is essential. Reaching the right audience with your message maximizes the chances of conversions, directly influencing ROAS. Poorly defined targeting can lead to wasted ad spend and a lower return.
Ad Quality and Relevance
The quality and relevance of your ads are paramount. Compelling ad copy and visuals that resonate with your target audience improve click-through rates and conversion rates, positively impacting ROAS.
Landing Page Experience
A seamless landing page experience is vital. A well-designed landing page that aligns with the ad’s message encourages conversions. A confusing or irrelevant landing page can deter users, negatively impacting ROAS.
Seasonality and Timing
Seasonality and timing also influence ROAS. Consumer behavior and purchasing patterns fluctuate throughout the year. Adapting campaigns to align with peak seasons can maximize returns.
Using ROAS to Optimize Your Ad Campaigns
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) is a crucial metric for evaluating and refining your advertising strategies. A strong understanding of your ROAS allows for data-driven decisions to maximize the effectiveness of your campaigns.
Regularly monitoring your ROAS can highlight areas for improvement. For example, a low ROAS for specific keywords may indicate the need for bid adjustments or revised targeting. Conversely, a high ROAS suggests potential for increased investment to scale successful campaigns.
A/B testing ad creatives with different messaging, visuals, and calls to action can provide valuable insights into which variations yield the best ROAS. Analyzing performance data across different channels enables strategic budget allocation towards the platforms delivering the highest returns.
Leveraging ROAS data helps refine targeting parameters. By identifying the demographics, interests, or behaviors associated with the highest ROAS, you can focus your ad spend on reaching the most profitable audience segments.
Setting Realistic ROAS Targets
Setting realistic ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) targets is crucial for successful advertising campaigns. A target that’s too high can lead to missed opportunities, while a target that’s too low might not maximize profitability.
Several factors influence a realistic ROAS target, including:
- Industry: ROAS benchmarks vary significantly across industries. Research your industry’s average ROAS to gain a starting point.
- Profit Margins: Higher profit margins allow for more flexibility with ROAS targets.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): If your CLTV is high, you can afford a lower initial ROAS, focusing on acquiring customers even if the immediate return is smaller.
- Campaign Stage: New campaigns often have a lower ROAS while they gather data and optimize. Mature campaigns should aim for higher, more stable ROAS.
Start with conservative targets and gradually increase them as you optimize your campaigns and gain a better understanding of your performance. Regularly analyze your data and adjust your targets accordingly to maximize profitability.
Common ROAS Mistakes to Avoid

Several common pitfalls can hinder your ROAS performance. Avoiding these mistakes is crucial for maximizing your advertising budget’s effectiveness.
Focusing Solely on a High ROAS
While a high ROAS is desirable, focusing exclusively on this metric can stifle growth. Sometimes, lowering your target ROAS can significantly increase your overall revenue.
Ignoring Attribution
Accurate attribution is vital. Not properly tracking where your conversions are coming from can lead to misinformed decisions and wasted ad spend.
Neglecting Data Analysis
Regularly analyze your campaigns. Failing to identify trends and adjust strategies based on data can result in a suboptimal ROAS.
Setting Unrealistic Expectations
Benchmarking your ROAS against competitors can be helpful, but understand that each business is unique. Setting unrealistic ROAS targets can lead to frustration and inefficient spending.
The Relationship Between ROAS and Other Metrics
ROAS doesn’t exist in a vacuum. It’s intrinsically linked to other key performance indicators (KPIs) that provide a more holistic view of your advertising performance. Understanding these relationships is crucial for effective campaign optimization.
Conversion Rate: A higher conversion rate directly impacts ROAS. More conversions from the same ad spend mean a higher return. Improving your website’s user experience or refining your targeting can boost conversion rates and, consequently, ROAS.
Average Order Value (AOV): AOV and ROAS are also closely related. If your AOV increases, your ROAS will likely increase as well, assuming your ad spend and conversion rate remain constant. Strategies like upselling and cross-selling can help increase AOV.
Cost Per Click (CPC): CPC influences ROAS inversely. A lower CPC generally leads to a higher ROAS, as you’re spending less to acquire each click. Effective keyword targeting and bid management are key to controlling CPC.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): While not directly reflected in ROAS calculations, CLTV is a crucial consideration. A high CLTV can justify a lower initial ROAS, especially if you’re focused on long-term customer relationships.
ROAS vs. ROI: Key Differences
While both Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) and Return on Investment (ROI) measure profitability, they do so with different scopes. ROAS focuses specifically on the return generated from advertising campaigns. It measures the revenue earned for every dollar spent on advertising.
ROI, on the other hand, provides a broader perspective on profitability. It considers the overall return from all investments in a business, including advertising, but also encompassing other factors like operational costs, salaries, and overhead. Therefore, ROI offers a more holistic view of a business’s financial performance.
A simple analogy can illustrate this difference: imagine a farmer planting a specific crop. ROAS would measure the return from that single crop, while ROI would represent the return from the entire farm operation, including all crops, livestock, and other associated expenses.
Understanding this key difference is crucial for effective performance analysis. ROAS helps optimize specific advertising campaigns, while ROI provides a broader evaluation of overall business profitability.
Advanced ROAS Strategies

Once you have a firm grasp of basic ROAS principles, you can explore more advanced strategies to further optimize your campaigns. These strategies often involve a deeper understanding of your target audience, data analytics, and bidding automation.
Predictive Bidding
Leveraging predictive bidding allows you to use historical data and machine learning to forecast future performance and automatically adjust bids accordingly. This can significantly improve ROAS by optimizing bids for conversions rather than clicks.
Audience Segmentation and Targeting
Refining your audience segmentation is crucial. By creating highly targeted campaigns based on demographics, behavior, and interests, you can reach the most valuable customers and maximize your return on ad spend. Consider utilizing custom audiences and lookalike audiences to reach users similar to your highest-converting segments.
A/B Testing Ad Creatives
Continuously A/B test different ad creatives to determine which resonates best with your audience. Test variations in copy, imagery, and call to actions to identify the elements that drive the highest conversion rates and ultimately, the best ROAS.